Neuro-Oncology
Choroid plexus tumors of childhood
Jan. 14, 2025
MedLink®, LLC
3525 Del Mar Heights Rd, Ste 304
San Diego, CA 92130-2122
Toll Free (U.S. + Canada): 800-452-2400
US Number: +1-619-640-4660
Support: service@medlink.com
Editor: editor@medlink.com
ISSN: 2831-9125
Toll Free (U.S. + Canada): 800-452-2400
US Number: +1-619-640-4660
Support: service@medlink.com
Editor: editor@medlink.com
ISSN: 2831-9125
Worddefinition
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti quos dolores et quas.
Nemaline myopathy is probably the most common of the congenital myopathies and can present at any age. As the known causative gene mutations expand, the classification system continues to evolve.
|
• Nemaline myopathy is the most common of the congenital myopathies. | |
|
• Nemaline myopathy can present at any age with proximal muscle weakness, respiratory insufficiency, or bulbar dysfunction. | |
|
• Childhood forms of nemaline myopathy are caused by mutations in numerous genes encoding muscle thin filaments. | |
|
• Adult forms of nemaline myopathy can be more rapidly progressive and may be caused by immune dysregulation. |
Nemaline myopathy was first described in 1963 by investigators from the United States and Canada (18; 117). Nemaline myopathy is defined by a particular ultrastructural change on muscle biopsy: the finding of thread-shaped structures in muscle fibers, which are known as nemaline bodies, or rods (from the Greek nema, meaning thread).
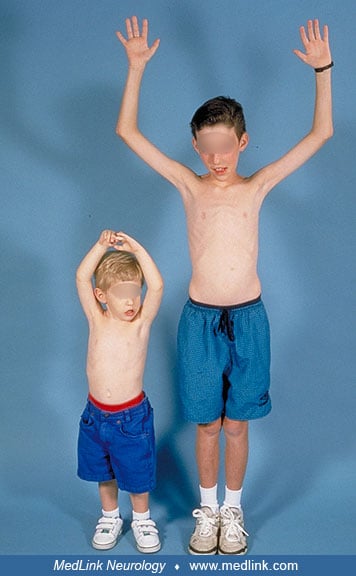
Children with nemaline myopathy usually present with muscle weakness and hypotonia, which in most instances are apparent from the neonatal period or early infancy. The most severe (and probably most uncommon) form is that presenting as the fetal akinesia sequence (63).
The severe congenital form of nemaline myopathy manifests at delivery with severe hypotonia, minimal limb movement, and poor respiratory effort. Polyhydramnios and decreased fetal movements in pregnancy are common (101). Bulbar weakness causes poor feeding and recurrent aspiration. Early mortality is common and is usually due to respiratory insufficiency or aspiration pneumonia, although a minority of infants with severe generalized weakness survives long-term (71; 99; 07).
An intermediate form of nemaline myopathy was recognized in prior classification schemes; however, this category was clinically impractical and had no genotype-phenotype correlation, and thus has been combined into the typical form in the current classification system (65).
The mild or typical congenital form of nemaline myopathy is probably the most common form of this disease and usually presents in the neonatal period or first year of life with hypotonia, weakness, and feeding difficulties. Spontaneous antigravity movements are present and respiratory involvement is less prominent. Some weakness of the respiratory musculature is usual but may be subclinical or manifest only as frequent lower respiratory tract infections or silent nocturnal hypoventilation. A minority of cases presents after one year of age with delay of gross motor milestones, an abnormal waddling gait, or bulbar weakness manifesting as hypernasal speech or swallowing difficulties. Weakness is usually proximal at presentation, but late distal involvement in seen in approximately 20% of patients (101). Most patients survive into late childhood and adulthood, with static or slowly progressive weakness, and are able to lead an independent, active life.
Childhood-onset nemaline myopathy presents with symmetrical distal lower limb weakness in early childhood, or less commonly with slowed limb movements (61; 103). Subsequent development of proximal weakness and wasting is associated in some cases, with progressive bulbar involvement and loss of ambulation by the age of 40 years.
More variability is seen in the late- or adult-onset form of nemaline myopathy, sometimes referred to as sporadic late-onset nemaline myopathy (SLONM), which presents between 20 and 50 years of age with rapidly progressive generalized limb girdle weakness and myalgia, usually without antecedent symptoms or family history (101). Cases can be associated with a monoclonal gammopathy, early HIV infection (65), or autoimmune disease (131). Atypical cases present with cardiomyopathy, or the “dropped head” syndrome. Respiratory involvement is uncommon, but occasional cases of nemaline myopathy present with adult-onset respiratory failure (57).
Nemaline myopathy affects the proximal limb muscles most severely, but all skeletal muscles, including the diaphragm, are involved. Muscle wasting is not invariable, but older children and adults are commonly slender. Proximal weakness is reflected in a wadding gait in ambulant patients. In adult-onset cases, initial distal weakness with foot drop and progressive gait abnormalities may be followed by later evolution of proximal involvement (61). In a minority of sporadic cases, weakness and joint contractures occur in a predominantly scapulohumeral distribution.
In the congenital forms of nemaline myopathy, the face is myopathic and expressionless, the mouth tent-shaped, and the palate high-arched.
There may be retrognathia or relative micrognathia due to abnormal muscle stresses on the developing mandible. The extraocular muscles are usually spared. Generally, the finding of external ophthalmoplegia should raise suspicion of mitochondrial disease (31), but ophthalmoplegia has been reported in a form of severe nemaline myopathy associated with recessive RYR1 mutations (54). Dysarthria and dysphagia are common. Bulbar involvement may also be reflected in a hypernasal voice and wasting of the tongue. Weakness of the neck flexors causes difficulty in lifting the head against gravity when supine and weakness of the extensors presents as dropped head syndrome while standing. Peripherally, poor muscle bulk is associated with depressed or absent deep tendon reflexes. Gross motor milestones are delayed, but most patients are otherwise developmentally normal.
Respiratory involvement is virtually universal in congenital nemaline myopathy and is frequent in patients with onset in later life. In infancy, respiratory and limb weakness are generally similar in degree. Chest deformity may be present at birth or develop with increasing age. The variant of nemaline myopathy seen in the North American Amish community is known as “chicken breast disease” because of its frequent association with preterminal pectus carinatum (49). In older patients, subclinical restriction of respiratory capacity may develop as a result of respiratory muscle weakness, sleep apnea, poor clearance of secretions, and scoliosis. Nocturnal hypoxia places patients at risk of sudden respiratory failure with intercurrent infections (134; 106; 40).
Infants with congenital nemaline myopathy commonly have feeding difficulties and failure to thrive (101).
Myocardial involvement is unusual in congenital nemaline myopathy (101). A thorough review of the literature completed by Finsterer and Stollberger catalogs the cardiac manifestations in patients with nemaline myopathy, which include cardiomyopathy and cor pulmonale (28).
Arthrogryposis is occasionally reported in congenital nemaline myopathy, presumably as a result of decreased movement in utero (13; 101). In the Amish form of nemaline myopathy described by Johnston and colleagues, mild congenital contractures of the shoulders and hips progressed over the first few months of life in association with increasing hypotonia and weakness (49). Joint hypermobility may be seen in hypotonic infants and children with nemaline myopathy, but development of distal and large-joint contractures, and scoliosis, is common with increasing age. The rigid-spine syndrome is occasionally seen (134). Other uncommon manifestations include congenital fractures (14; 101), arachnodactyly, and clinodactyly.
The central nervous system and cognition are usually minimally or unaffected in nemaline myopathy (115; 134). Generalized myoclonus and minipolymyoclonus have rarely been described in congenital nemaline myopathy (17; 11), whereas the Amish variant of nemaline myopathy is marked by “abnormal vibratory fetal movements” and excessive neonatal jitteriness (49).
Prognosis in nemaline myopathy is dependent on the severity of weakness of the respiratory, bulbar, and limb muscles. Early mortality is common, most often during the first year of life, and is almost invariably related to respiratory insufficiency. Arthrogryposis, neonatal respiratory failure, and failure to achieve early motor milestones are associated with a greater risk of early mortality (101). Surviving patients are at risk of recurrent pneumonia, aspiration, and chronic respiratory insufficiency (72; 41; 134). Prolonged respiratory insufficiency with chronic hypercarbia may lead to cor pulmonale. In such cases, nighttime noninvasive ventilation improves daytime oxygenation and exercise capacity, reduces cor pulmonale and may prolong survival. Other complications of nemaline myopathy include failure to thrive, bulbar weakness with dysarthria and speech delay, and orthopedic deformities including contractures and scoliosis (12).
JB was the first child of nonconsanguineous parents. The pregnancy was complicated by mild polyhydramnios. He was delivered at term by Cesarean section because of fetal distress, with a birth weight of 3200 gm. He required oxygen therapy for the first four days of life and had early difficulty with feeding due to a weak suck. Gastroesophageal reflux was identified on a barium swallow. Weight gain improved after the early introduction of solids.
From the first few days of life, his cry was weak and he drooled excessively. His eyes closed incompletely in sleep. He sat at 5 months, crawled at 1 year, and took his first steps at 20 months of age. During infancy, he had recurrent episodes of choking and numerous lower respiratory tract infections. His speech was markedly dysarthric.
When first seen by a neurologist at 20 months of age, he was thin, with poor muscle bulk, and a myopathic face. There was marked head lag and generalized hypotonia. Muscle power was decreased in all extremities and the tendon reflexes were hypoactive. Nerve conduction studies were normal. Needle electromyography revealed low-amplitude polyphasic motor unit action potentials. The serum creatine kinase was normal. On muscle biopsy, there was increased fiber size variation, with type 1 fiber predominance. The Gomori trichrome stain revealed nemaline bodies in most fibers. No intranuclear rods were seen on electron microscopy.
Echocardiography was unremarkable. A sleep study demonstrated occasional episodes of sleep apnea without significant desaturation.
With increasing age, a decrease in the frequency of his chest infections was accompanied by decreasing dysphagia and dysarthria. No progression of his weakness was apparent and his endurance appeared to improve. At 3 years of age he continued to make gains in all developmental spheres.
Nemaline myopathy is defined by the presence of nemaline rods in myofibers, when present in the appropriate clinical setting of muscle weakness.
Genetics. A growing number of genetic loci have now been identified for childhood-onset nemaline myopathy, all of which are associated with the thin filament of the sarcomere in skeletal muscle whether by encoding structures proteins or regulatory proteins. Mutations in NEB and ACTA1 are the most common, though many other affected genes have been described (in order of discovery) alpha-tropomyosin slow (gamma tropomyosin) (TPM3, chromosome 1q21-23) (62); nebulin (NEB, chromosome 2q21.2-22) (93); alpha-actin (ACTA1, chromosome 1q42.1) (90); troponin T1 (TNNT1, chromosome 19q13.4) (49); beta tropomyosin (TPM2, chromosome 9p13.2) (23); cofilin-2 (CFL2, chromosome 14q12) (01); KBTBD13 (chromosome 15q22) (103); ryanodine (RYR1) (54); KLHL40 (97); KLHL41 (37); and LMOD3 (leiomodin-3, chromosome 3p14.1) (144). The first six of these encode protein components of thin filaments of muscle fibers. KBTBD13 (BTB and Kelch domain containing 13 protein), KLHL40, and KLHL41 are members of the BTB/Kelch family, which is known to be involved in protein ubiquitination, although its exact function is unclear. RYR1 encodes the principal sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-release channel, which plays a crucial role in excitation-contraction coupling. Leiomodin is a member of the tropomodulin protein family. MYPN mutations can cause nemaline myopathy and also cardiomyopathy (69). A case report suggests that RYR3 may be an additional causative gene (85). Myopathic changes with nemaline rods were seen in a patient with a filamin C mutation (26).
Mutations in several of these genes also cause other muscle disorders.
The mode of inheritance of nemaline myopathy is variable. Both autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance patterns exist, sometimes even for different mutations in the same gene.
Genotype-phenotype correlation in nemaline myopathy has been extensively studied. Most typical congenital cases are thought to be due to nebulin mutations, but nebulin nemaline myopathy can present at any point in life (138). The clinical phenotype of nebulin myopathy has been expanded with descriptions of a distal myopathy caused by recessive mutations in this gene, which can present as early as the first decade (137; 67). Actin mutations may be associated with a more severe clinical phenotype and with intranuclear rods, but marked phenotypic variability can be seen within kindreds (121; 43; 03; 36; 138). Actin mutations can also cause a milder dominant myopathy with cores, actin filament aggregate myopathy, and congenital fiber type disproportion (52; 60). There is a single report of actin aggregate myopathy in association with osteosclerosis and other morphologic abnormalities (05). Regardless of histopathologic phenotype, most individuals with actin mutations have severe muscle weakness, many dying in the first year of life (60). Cardiac function is generally normal in actin nemaline myopathy. This may relate to variable expression of cardiac and skeletal muscle isoforms of actin at various points in ontogenesis (42). Overall, the mildest phenotype seems to be the childhood-onset form of nemaline myopathy associated with dominant mutations of the alpha-tropomyosin gene, TPM3 (62; 94). Mutations in this gene have also been linked to congenital fiber type disproportion and cap myopathy (22; 66).
Rare, distinctive phenotypes associated with nemaline myopathy include the Amish form of the disease, which is associated with tremor, contractures, and progressive muscle weakness (49). Nemaline myopathy caused by dominant KBTBD13 mutations presents from early childhood with peculiarly slow voluntary movements and relative sparing of the facial and respiratory muscles (35; 103). Nemaline myopathy with cores may be associated with ryanodine receptor gene mutations (78; 107), or with mutations in KBTBD13 (103).
The cause of sporadic, late-onset nemaline myopathy is unknown, but the links with monoclonal gammopathy and with early HIV infection (during the phase of retained immunocompetence) have suggested a possible disorder of immune regulation. This postulate is given weight by reports of improved strength, respiratory capacity, and function after treatment of sporadic, adult-onset nemaline myopathy with melphalan and autologous stem-cell transplantation (09; 130; 77).
Sporadic late-onset nemaline myopathy seems to be related, in part, to aberrant immune activation (81). Proteomic profiling in cases of SLONM show upregulation of proteins related to the immune system including proteins involved in MHCI, MHCII, antigen processing, phagocytosis, and B and/or T cell function.
Pathophysiology. Alpha-actinin, an actin-binding protein, is the major component of the rods seen on histology, which constitute an extension of the sarcomeric Z-band (95; 48). Rods also contain nebulin, a thin filament protein (38), tropomyosin (122), and myotilin, a structural protein that cross-links to actin and has a role in formation and stabilization of Z-discs (109). Nebulin binds to actin, and the size of nebulin correlates with actin filament length, suggesting that nebulin may determine the length of the thin filaments during myofibrillogenesis (24). Nebulin may also act to increase activation of thin filaments and increase the force and efficiency of muscle contraction by altering crossbridge cycling kinetics (15; 34; 92). Studies on the nebulin knock-out mouse suggest that nebulin acts to regulate thin filament length and maintain Z-band width and myofibrillar connectivity, and that it may increase thin filament activation (15; 127).
Seven thin filament proteins are mutated in differing forms of nemaline myopathy. Most attach to the muscle Z-band, suggesting that rod formation may follow disruption of the point of attachment of muscle proteins to actin or alpha-actinin (46; 58). Mutations in ACTA1 may alter the conformation or stability of actin monomers or polymers, directly or through perturbation of actin-actin association or by disruption of binding with other proteins (45; 133; 76). Expression of actin mutants in myotubes results in apoptotic cell death (128). In a transgenic mouse model, disease severity seems to correlate with mutation load (96). Tropomyosin also has a role in stabilization of filamentous actin and may enhance actin polymerization. Skeletal muscle expresses 3 tropomyosin (Tm) isoforms from separate genes: alphaTm(fast) (alphaTm, TPM1), betaTm (TPM2), and alphaTm(slow) (gammaTm, TPM3). In an in-vitro model of alpha tropomyosin (TPM3)-related nemaline myopathy, mutant TPM3 was expressed and incorporated normally into striated muscle sarcomeres. Rod formation was seen only after active muscle contraction, suggesting that load-dependent processes are required for creation of nemaline bodies (73). In other studies, however, transfection of mutant TPM3 into myoblasts resulted in reduced incorporation into fibers and disruption of the filamentous actin network (44).
The level of betaTm, but not alphaTm(fast) protein, is reduced in human patients with mutations in alphaTm(slow) and in a transgenic mouse model of alphaTm(slow)(Met9Arg) nemaline myopathy, and the onset of alphaTm(slow)(Met9Arg) expression coincides with the decline of betaTm. Reduction of betaTm levels is independent of the degree of pathology (rods) within a muscle and is detected before the onset of muscle weakness. Alpha-tropomyosin(slow) dimers, composed of equal ratios of wild-type and M9R-alpha-tropomyosin(slow), are the dominant tropomyosin species in TPM3 nemaline myopathy. Myopathy-related slow-fiber predominance likely contributes to the severity of weakness in TPM3 nemaline myopathy because of increased proportions of fibers that express the mutant protein (44). The alphaTm(slow)(Met9Arg) mutation also acts to reduce the formation of the preferred alpha/beta heterodimer. This may alter sarcomeric thin filament dynamics, causing muscle weakness in nemaline myopathy (19). Developmental expression studies show that alpha-tropomyosin(slow) is not expressed at significant levels until after birth. This likely explains the later onset of TPM3 nemaline myopathy (44).
Nemaline myopathy related to troponin T1 deficiency is associated with complete loss of slow skeletal muscle troponin T, selective atrophy of type 1 fibers, and relative insensitivity to calcium (47). The nonsense mutation at codon Glu180 in this disorder causes production of a truncated troponin T protein, which has a decreased affinity for binding to tropomyosin because of loss of one of two tropomyosin binding sites. This truncated slow troponin T protein is rapidly degraded (142). The giant nebulin gene comprises 183 exons and contains four regions with alternatively spliced exons, giving rise to a number of different transcripts that vary among muscle types and among muscles of different developmental stages. Nebulin knockout mice have shortened thin filaments with abnormally wide Z-discs, resulting in decreased contractility (143). Extensive alternative splicing of NEB may explain why patients with nemaline myopathy and homozygous truncating mutations show expression of the carboxy-terminus of the nebulin protein, contrary to expectation, and may explain why severe phenotypes are rare among patients with two truncating mutations (24). Nebulin mutations are located through constitutively and alternatively expressed exons throughout the NEB gene, with no obvious mutational hotspots (68). Cofilin-2 is a small actin-binding protein predominantly expressed at sarcomeres. Its role in muscle development and function is unclear, but preservation of sarcomeric integrity may be contingent on developmentally specific expression of cofilin isoforms (01; 02).
Nemaline myopathy with cores is seen with ryanodine receptor gene mutations (78; 107) and with the form of nemaline myopathy associated with mutations in KBTBD13 (103).
Other proteins of the sarcolemmal cytoskeleton have also been studied in nemaline myopathy. Rods do not contain titin (112) or nebulin. Desmin is increased in fibers containing rods (126; 105) and accumulates at the periphery of rods in some patients (112). Sarcolemmal dystrophin is normal in nemaline myopathy, but spectrin studies may be abnormal in severe cases (111).
Increased expression of cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, a nuclear protein that may act as a negative regulator of cardiac-specific gene protein, has been identified in nemaline myopathy, a finding that is of unclear significance but may reflect persistent expression or upregulation of fetal muscle proteins (100). In actin nemaline myopathy, upregulation of a fetal cardiac actin isoform may ameliorate muscle weakness (89). Developmental regulation of muscle protein expression may affect presentation of a number of forms of nemaline myopathy (47; 89; 02).
On immunocytochemical examination, nemaline bodies consist primarily of alpha-actinin (48) and have structural similarity to the Z-lines of muscle sarcomeres. Antibodies to alpha-actinin 2 (ACTN2) and alpha-actinin 3 (ACTN3) stain Z-lines and rods in skeletal muscle. Rod composition is usually fiber-type dependent, with alpha-actinin 2 being present in rods in all fibers, whereas alpha-actinin 3 is present only in rods in type 2 muscle fibers (87), but this is not absolute. In some cases, alpha-actinin isoforms within rods do not conform to fiber-type specific proteins expressed in other parts of the myofibril, suggesting the possibility of fiber-type conversion. This is supported by the finding, in some muscle fibers, of coexpression of fast and slow myosin isoforms (111; 100). Immunocytochemical studies also demonstrate myotilin immunoreactivity in rods of slow and fast twitch fibers (109).
Gene expression studies in nemaline myopathy have identified downregulation of transcripts of enzymes of glucose and glycogen metabolism, altered transcription of genes involved in calcium homeostasis, and increased expression of structural proteins involved in muscle fibrosis (104). The significance of these changes, which occur downstream from the primary molecular abnormalities of nemaline myopathy, is unclear at this time.
Respiratory chain enzyme analysis has shown complex 1 deficiency in cases of nemaline myopathy related both to nebulin and actin mutations (64; 136).
The cellular mechanism underlying loss of muscle strength in nemaline myopathy is poorly understood. Weakness may be due to myocyte loss, abnormal fiber-typing, or myocyte immaturity. Sarcomeric disorganization, with an excess of thin filaments, is common in congenital nemaline myopathy (32; 43; 100) and may become more marked on serial biopsies (139; 100). Sarcomeric disarray may result from altered interaction of mutated thin filaments with Z-line proteins such as alpha-actinin or tropomodulin, resulting in formation of nemaline bodies and loss of contractility (79; 45; 01; 44). Alternatively, weakness may result from desensitization of calcium-activated muscle contraction, or temporal alterations in the contraction-relaxation cycle of skeletal muscles, resulting in altered regulation of force production (73; 74). In actin nemaline myopathy, weakness may be partially compensated by upregulation of alpha-cardiac actin, the skeletal muscle fetal actin isoform (89).
Type 1 fiber predominance in nemaline myopathy may be due to abnormalities of fiber type maturation, active conversion of type 2 to type 1 fibers, or a combination of these processes (132; 116). An increase in slow oxidative fibers may occur as a means of preserving muscle strength, oxidative metabolism being more energy efficient (123). In a mouse model of alpha-tropomyosin deficiency, exercise does not appear to worsen the pathologic phenotype of nemaline myopathy, but it does alter fiber-type conversion in a muscle- and fiber-type specific manner (83). A minority of patients with nemaline myopathy has no alteration of fiber typing or fiber size variation on biopsy (139). This pathological heterogeneity may reflect variable pathogenesis of rod formation in different genetic subtypes of nemaline myopathy. Rod composition and actin dynamics differ in genetic and secondary forms of nemaline myopathy, suggesting that rod formation represents a common morphological endpoint of a variety of different pathological processes (129).
The incidence of nemaline myopathy is estimated to affect 1 in 50,000 live births. In the Amish community, the incidence may be as high as 1 in 500, and this population shows increased frequency of nemaline myopathy related to troponin T mutations (49). Nemaline myopathy occurs in all races and ethnic groups. Nebulin mutations appear to be relatively common in Ashkenazi Jewish populations (04). Overall, it is estimated that up to 50% of all cases are due to nebulin mutations (93), whereas at least 20% of cases are related to mutations in the actin gene (90). Sporadic occurrence is not unusual and is presumably due to new dominant mutations or autosomal recessive inheritance.
With the identification of causative mutations at numerous genetic loci, mutation analysis and genetic counseling may now be feasible in some families, using blood, chorionic villus, or amniotic fluid samples. However, the large size of the nebulin gene, the large number of other causative genes, and the existence of other (as yet unidentified) causative genetic loci make molecular testing problematic at the present time. Additionally, no reliable clinical predictors of likely inheritance mode have yet been identified. Histologic examination of muscle biopsies does not reliably distinguish between autosomal dominant and recessive forms of nemaline myopathy, or between severely and mildly affected patients (100). Fetal muscle biopsy is not useful for prenatal diagnosis, as immature Z-bands in developing muscle may resemble rods.
In severely affected neonates, the hypotonia and weakness of nemaline myopathy must be distinguished from the central hypotonia caused by structural disorders or such genetic conditions as the Prader-Willi syndrome. Muscle weakness is seen in other congenital myopathies (such as myotubular myopathy), in Pompe disease, and in the congenital myasthenic syndromes and transient neonatal myasthenia gravis. Nemaline myopathy may also clinically resemble spinal muscular atrophy (55) and the congenital hypomyelinating neuropathies.
|
• Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in sporadic late-onset nemaline myopathy | |
|
• Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) in sporadic late-onset nemaline myopathy autoimmune disease in sporadic late-onset nemaline myopathy |
Muscle enzymes are usually normal in nemaline myopathy but may be mildly elevated. Electromyography may show normal motor unit potentials or small, short-duration action potentials consistent with a myopathic process (134; 101). Nerve conduction studies are usually normal.
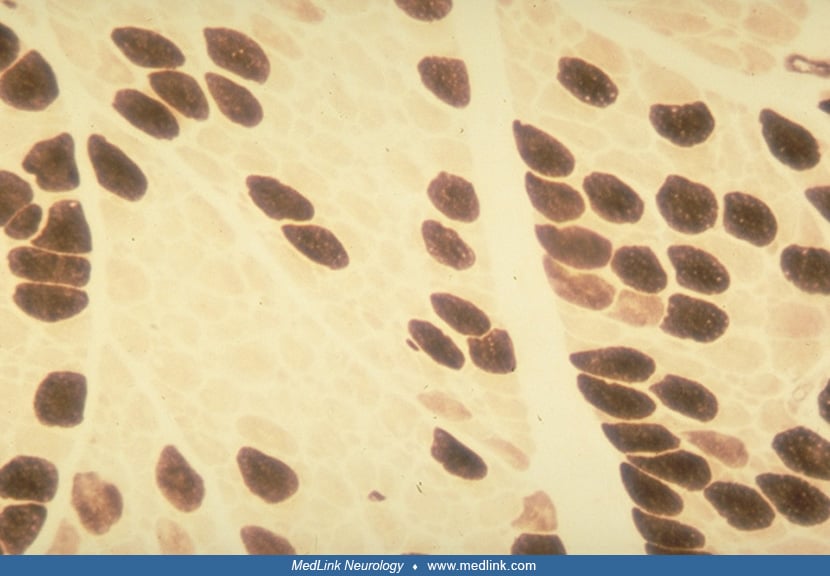
Diagnosis depends on the finding of nemaline rods on muscle biopsy. Nemaline bodies are best seen with the modified Gomori trichrome stain of fresh frozen sections; they look dark purple and granular under the light microscope.
Rods are most frequently located in the subsarcolemmal region. Rod number varies widely between patients, between different muscles in a single patient, and even between different parts of a muscle (84; 114). The number and distribution of nemaline bodies do not tend to correlate with age of presentation or clinical severity of nemaline myopathy (116; 100). In most patients, numerous rods are seen in most or all extrafusal muscle fibers (114), but in some cases they are apparent only in type 1 fibers. Intrafusal fibers do not contain rods (117). On electron microscopy, rods are often associated with marked sarcomeric disorganization and loss of normal sarcomeric registration (43; 100). Not infrequently, however, areas of complete sarcomeric disarray will abut relatively normal sarcomeres, a phenomenon that remains poorly understood. Numerous nemaline bodies, glycogen accumulation, and marked sarcomeric disruption are more common in nemaline myopathy associated with mutations in skeletal alpha-actin, whereas nemaline myopathy due to mutations in alpha-tropomyosin may be characterized by preferential rod formation in, and atrophy of, type 1 fibers (100).
In most patients nemaline bodies are confined to the sarcoplasm. Rods are occasionally also seen in sarcomeric nuclei. The presence of intranuclear rods appears to correlate with poor prognosis: they have been seen both in cases of severe neonatal nemaline myopathy (98; 08; 33) and in a minority of progressive adult cases (25; 91). Intranuclear rods may be more common in actin nemaline myopathy (138; 56).
Predominance of type 1 fibers is common in nemaline myopathy, often with a decrease in type 1 fiber diameter (30; 75). Internal nuclei are common and fiber splitting is occasionally seen. These changes tend to progress with age. Inflammatory changes are not characteristic of nemaline myopathy, but occasional necrotic or regenerating fibers may be seen in patients with progressive adult-onset disease and reactivity for MHCI by immunohistochemistry can be seen in fibers with rods as well as adjacent nonatrophic fibers (81). Acid phosphatase activity is also increased in patients with rapid progression (86; 11). Progressive muscle fibrosis may be seen on serial muscle biopsies (139; 100).
Nemaline bodies are not pathognomonic of nemaline myopathy. Nemaline bodies have been reported in normal human extraocular muscle (80; 70), with aging, and after tenotomy and radiotherapy. Rod formation can represent a nonspecific response to muscle damage. Nemaline bodies have been reported in a number of neuromuscular and unrelated conditions, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, polymyositis, oculopharyngeal and limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, chorea-acanthocytosis, neurosarcoidosis, and diploid/triploid mosaicism (118; 39; 64; 125; 113). Nemaline bodies were identified in the muscle of a child with Timothy syndrome, a multisystem disorder with congenital heart disease, immune deficiency, intermittent hypoglycemia, cognitive abnormalities, and autism. Timothy syndrome is due to a mutation in a cardiac L-type calcium channel (120).
Ultrastructural changes suggestive of other congenital myopathies, such as cores, minicores, caps, or zebra bodies are commonly seen in patients with nemaline myopathy (53; 110; 20; 124; 01; 89). Cores are characteristically seen in the nemaline myopathies caused by ryanodine receptor gene mutations (78; 107) and KBTBD13 mutations (103). Nemaline myopathy has also been associated with congenital fiber-type disproportion (30; 75) and cap disease (124). Mutations in both actin and tropomyosin have been identified in patients with fiber-type disproportion without rod formation, expanding the clinical spectrum of myopathies associated with the genes (59; 16).
The diagnosis of nemaline myopathy is, therefore, not justified in the absence of a typical clinical picture. It may be that, in the congenital myopathies, common secondary changes in muscle develop in response to varied primary insults.
Other investigations to consider in patients with nemaline myopathy include electrocardiography and echocardiography in order to exclude the possibility of an associated cardiomyopathy. Pulmonary function tests identify subclinical respiratory disease and those at risk of acute decompensation with anesthesia or pneumonia. Sleep studies identify patients with nocturnal carbon dioxide retention and hypoventilation. Chronic pulmonary insufficiency may cause development of cor pulmonale (41). Serial testing of cardiac and pulmonary function is indicated, as there may be deterioration with increasing age.
Muscle MRI may have a place in diagnosis of nemaline myopathy and may help direct genetic testing. A report of muscle MRI in patients with actin and nebulin nemaline myopathy identified characteristic patterns of abnormality in both conditions. Patients with actin mutations had diffuse involvement of thigh and leg muscles, with relative sparing of the gastrocnemii, whereas nebulin nemaline myopathy was associated with selective involvement of the tibialis anterior and soleus, the thigh muscles showing changes only in nonambulant patients (51). Whether these patterns prove predictive in patients with an unknown genotype or just reflect disease severity remains to be seen.
Supportive therapy. No therapies can at this time alter the essential nature or clinical progression of the congenital myopathies. Treatment is, therefore, aimed at early diagnosis, maintenance of function, and treatment of complications. Standards of care for congenital myopathy are now available and should guide clinical management (141). Respiratory disease is the major cause of morbidity and mortality in nemaline myopathy. In neonatal cases, supportive therapy can be offered in the form of mechanical ventilation, but patients requiring respiratory support at this age have a generally poor prognosis (101). Long-term assisted ventilation has been undertaken in a small number of older patients with nemaline myopathy (115). Noninvasive nocturnal ventilation is an important therapeutic option in older patients with chronic respiratory failure and cor pulmonale. The onset of respiratory failure may be insidious (119), with rapid decompensation in respiratory and cardiac function with intercurrent respiratory tract infections. In some cases, brief periods of assisted ventilation during acute respiratory illnesses may prolong survival (106), although recovery to a point where ventilatory assistance can be withdrawn can be difficult to predict. Pulmonary infections should be treated promptly with chest physiotherapy and antibiotics. Immunizations, including those against pneumococcus and influenza, may help to minimize the incidence of pneumonia.
Bulbar dysfunction is common in nemaline myopathy and often causes aspiration of oral secretions. Evaluation of adequacy of the swallow should be a part of the initial assessment and should be reviewed if symptoms referable to aspiration are identified. Nutritional support is especially important in those with impaired bulbar function. Failure to thrive may be related both to poor intake and to the increased metabolic demands imposed by recurrent aspiration pneumonitis. Malnutrition has been implicated as a cause of significant morbidity in younger patients with nemaline myopathy (88). Nasogastric tube feedings or placement of a gastrostomy may be necessary to maintain nutrition in infants. Accelerated weight gain and improvement of respiratory function may follow gastrostomy with or without fundoplication (10).
Symptomatic cardiac involvement is uncommon in nemaline myopathy, but echocardiography is useful in identification of incipient cor pulmonale and prompt introduction of assisted ventilation. The QT interval should be assessed in children with nemaline myopathy and dysmorphic or autistic features in order to exclude the Timothy syndrome (120).
Physical therapy for nemaline myopathy should include daily passive range of motion exercises to prevent contracture formation. Exercise does not appear to worsen the pathologic phenotype of nemaline myopathy, but changes in muscle morphology after exercise are influenced by the causative mutation (83). Patients should be mobilized as soon as possible after surgery, as prolonged immobility may significantly exacerbate muscle weakness (101). One published murine study suggests that immobility may be associated with the reversible formation of additional nemaline bodies in muscle (50). Orthopedic intervention may be required in patients with congenital and acquired contractures, pathological fractures secondary to disuse osteopenia, and scoliosis. The timing of procedures is crucial in determining their efficacy and safety. Prior to any anesthesia or sedation, all patients should undergo a thorough preoperative assessment with consideration of potential anesthetic difficulties and respiratory reserve.
Drug therapy. The only specific treatment for the genetic forms of nemaline myopathy identified to date is L-tyrosine, a precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. L-tyrosine has been shown in rats to increase catecholamine production and release, improve reaction and attention time, and improve tolerance of physical stress, and, in some children with nemaline myopathy, appears to improves bulbar function and exercise tolerance when given orally at a dose of 250 to 3000 mg/day (102).
There is an array of early clinical and preclinical therapies being evaluated (11 such therapies are summarized in a study by Fisher) (29); however, all treatments at this time are supportive.
Sporadic late-onset nemaline myopathy first-line treatment consists of IVIg (82). Daratumumab (108), rituximab, methotrexate, and other agents generally considered to be cancer therapies have been reportedly used with varying levels of success, though the role of chemotherapy in this condition is currently controversial. Autologous stem cell transplant with or without chemotherapy in the setting of monoclonal gammopathy has also been recommended by several authors.
Labor and delivery in women with nemaline myopathy has generally been well tolerated. Cardiac and respiratory function should be monitored carefully throughout pregnancy, and there should be early consideration of appropriate means of anesthesia and delivery (135).
Malignant hyperthermia is a risk in congenital myopathies such as central core disease and in some muscular dystrophies. Nemaline myopathy has not been definitively associated with malignant hyperthermia to date (27), although bradycardia and slight hyperthermia have been reported during cardiac surgery (06). It is advisable to avoid neuromuscular blocking agents where possible (21), especially given the description of core-rod myopathies linking to genes for ryanodine receptor mutations (78; 107). Performance of pulmonary function tests, blood gas analysis, and intensive pre- and postoperative physiotherapy should be considered. Subclinical respiratory insufficiency may be unmasked by anesthesia and exacerbated by postoperative atelectasis and by spinal instrumentation (101).
All contributors' financial relationships have been reviewed and mitigated to ensure that this and every other article is free from commercial bias.
Yelena Wilson DO
Dr. Wilson of Akron Children's Hospital has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
See ProfileJennifer Baccon MD PhD MHCM
Dr. Baccon of Akron Children's Hospital and Northeast Ohio Medical University has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
See Profile
Harvey B Sarnat MS MD FRCPC
Dr. Sarnat of the University of Calgary has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
See ProfileNearly 3,000 illustrations, including video clips of neurologic disorders.
Every article is reviewed by our esteemed Editorial Board for accuracy and currency.
Full spectrum of neurology in 1,200 comprehensive articles.
Listen to MedLink on the go with Audio versions of each article.
MedLink®, LLC
3525 Del Mar Heights Rd, Ste 304
San Diego, CA 92130-2122
Toll Free (U.S. + Canada): 800-452-2400
US Number: +1-619-640-4660
Support: service@medlink.com
Editor: editor@medlink.com
ISSN: 2831-9125
Neuro-Oncology
Jan. 14, 2025
Neuromuscular Disorders
Dec. 29, 2024
Developmental Malformations
Dec. 26, 2024
Developmental Malformations
Dec. 26, 2024
General Child Neurology
Dec. 26, 2024
Developmental Malformations
Dec. 14, 2024
Developmental Malformations
Dec. 12, 2024
Neuromuscular Disorders
Dec. 09, 2024