- Clinical Categories
Neuro-Ophthalmology & Neuro-Otology
-

Media
Symptoms that lead to emergency department visits in patients with POTS
(Source: Cooperrider J, Kriegler J, Yunus S, Wilson R. A survey-based study examining differences in perception of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome between patients and primary care physicians. Cureus 2022;14[10]:e30167. Creative Commons Attribution [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
Most common occurring symptoms in patients with POTS
(Source: Cooperrider J, Kriegler J, Yunus S, Wilson R. A survey-based study examining differences in perception of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome between patients and primary care physicians. Cureus 2022;14[10]:e30167. Creative Commons Attribution [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

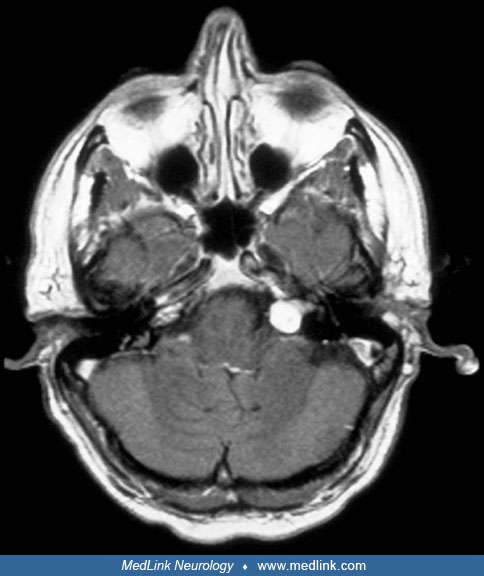
Media
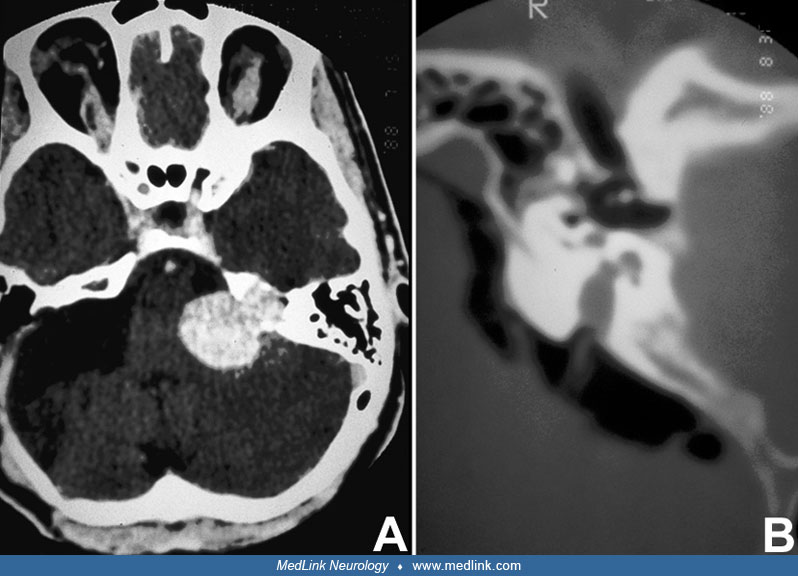
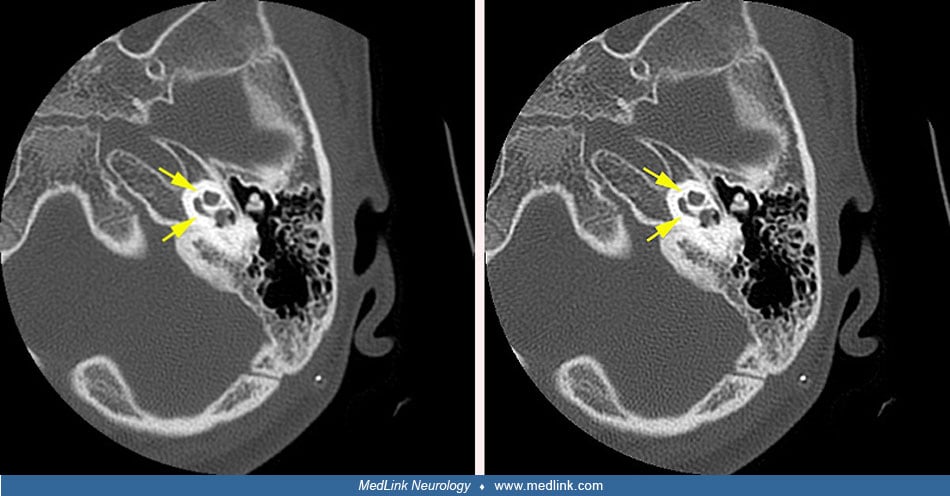
Involvement of the petrous part of the left temporal bone in otalgia (axial CT)
Axial CT scan showing involvement of the petrous part of the left temporal bone. The superior semicircular canal is surrounded by dysplasia. (Source: Sbai AA, Es-Salhi F, Tsen AA, Fahd Elayoubi. Otalgia revealing McCune-Albright syndrome: a case report. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2022;82:104706. Creative Commons Attribution [CC-BY] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
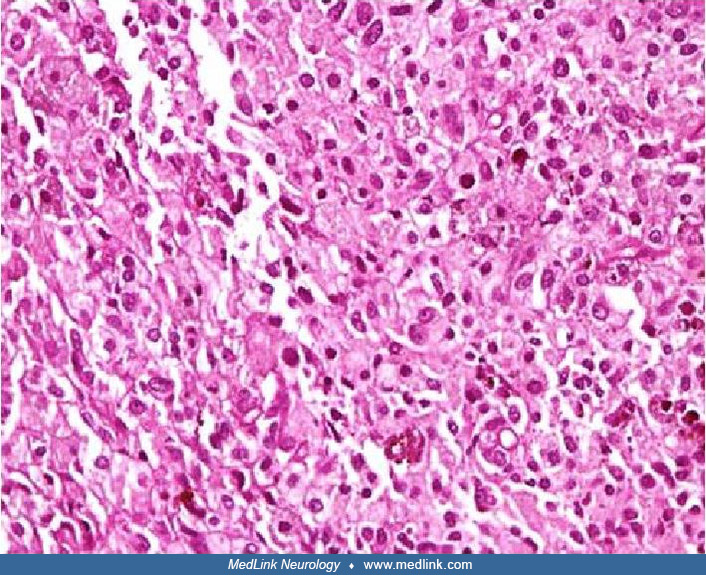
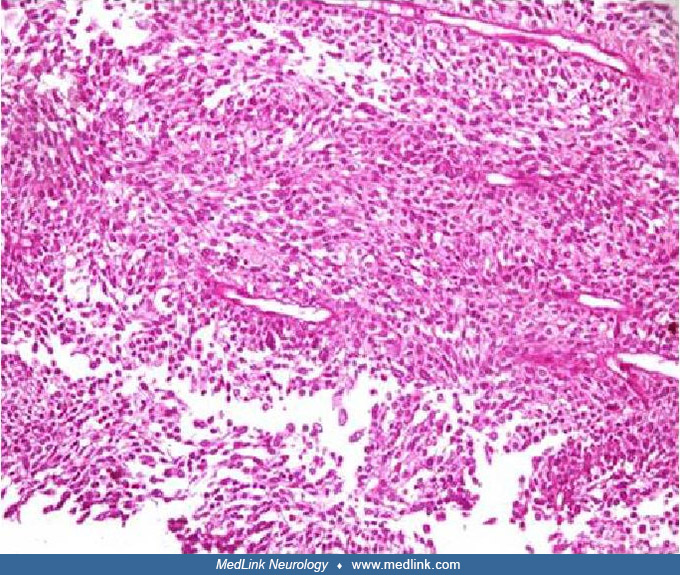
Right mastoid tumor histology in otalgia
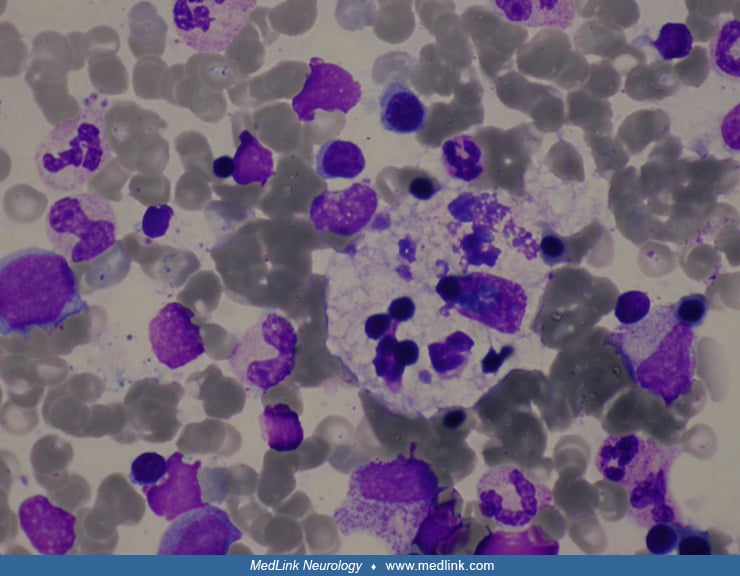
Histology of the right mastoid tumor (H&E) demonstrating malignant lymphoid cells with markedly pleomorphic and enlarged nuclei, small nucleoli, and scanty cytoplasm (white arrows). There are many mitoses and apoptotic bodies (white arrow heads). (Source: Jumaat AF, Gendeh H, Mohd Mustapha AW, Tan GC, Goh BS. Otalgia and facial nerve palsy: common symptoms revealing the uncommon pathology of middle ear lymphoma. Cureus 2022;14(5):e25023. Creative Commons Attribution [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

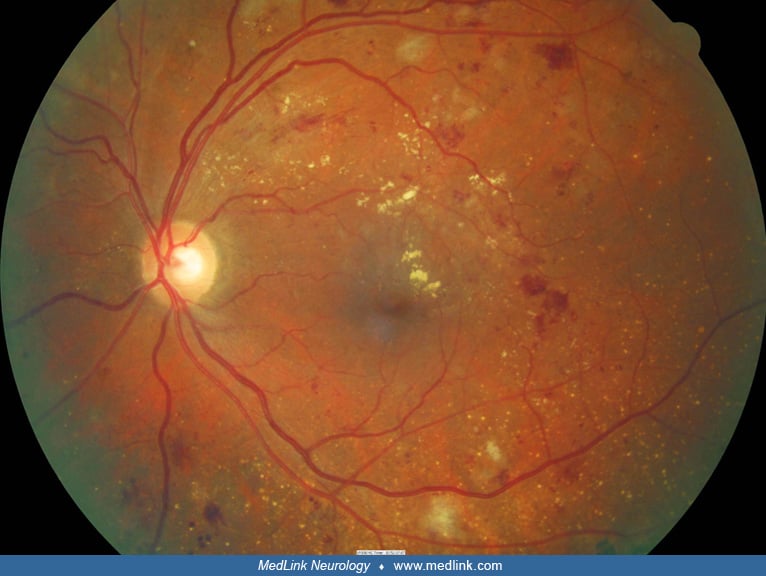
Media
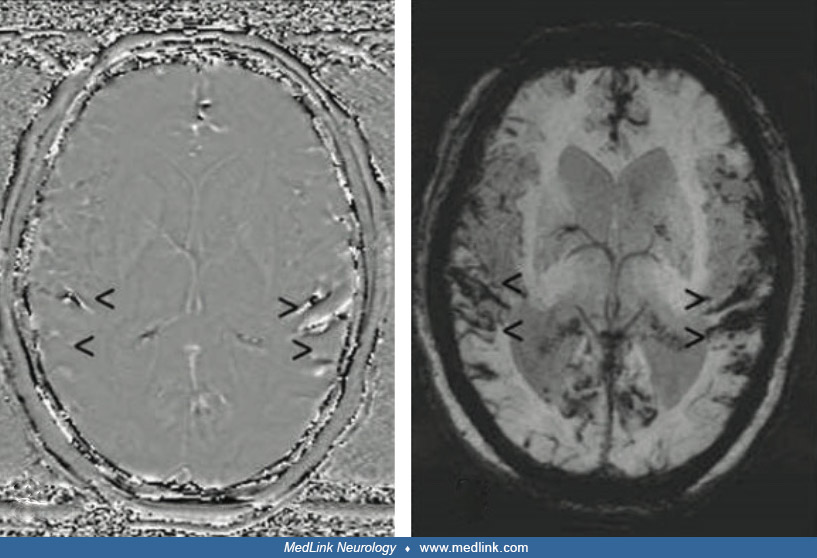
Internal auditory canal of a patient with herpes zoster oticus (MRI) (1)
Internal auditory canal MRI image of a patient with herpes zoster oticus. The post-contrast 3D-FLAIR MRI shows high-signal intensities of cochlea (long arrow), posterior semicircular canal, lateral semicircular canal (large arrow), and vestibule (arrowhead) in the right ear. (Source: Lee J, Choi JW, Kim CH. Features of audio-vestibular deficit and 3D-FLAIR temporal bone MRI in patients with herpes zoster oticus. Viruses 2022;14[11]:2568. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
Nonspecific findings on facial nerve conduction study in Ramsay-Hunt syndrome
A facial nerve conduction study revealed nonspecific findings. NCV = nerve conduction velocity. (Source: Hwang YS, Kim YS, Shin BS, Kang HG. Two cases of Ramsay-Hunt syndrome following varicella zoster viral meningitis in young immunocompetent men: case reports. BMC Neurol 2023;23[1]:43. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
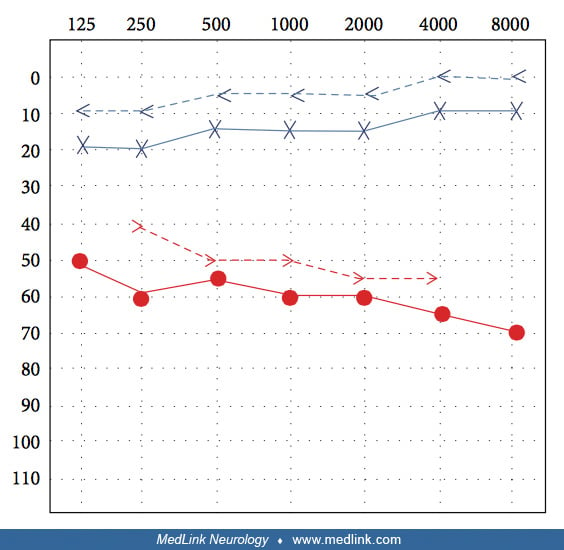
Pure-tone audiometry revealing high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss in Ramsay-Hunt syndrome (1)
Pure-tone audiometry revealing both increased air and bone conduction thresholds without an air-bone gap in the right ear, consistent with high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. (Source: Hwang YS, Kim YS, Shin BS, Kang HG. Two cases of Ramsay-Hunt syndrome following varicella zoster viral meningitis in young immunocompetent men: case reports. BMC Neurol 2023;23[1]:43. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
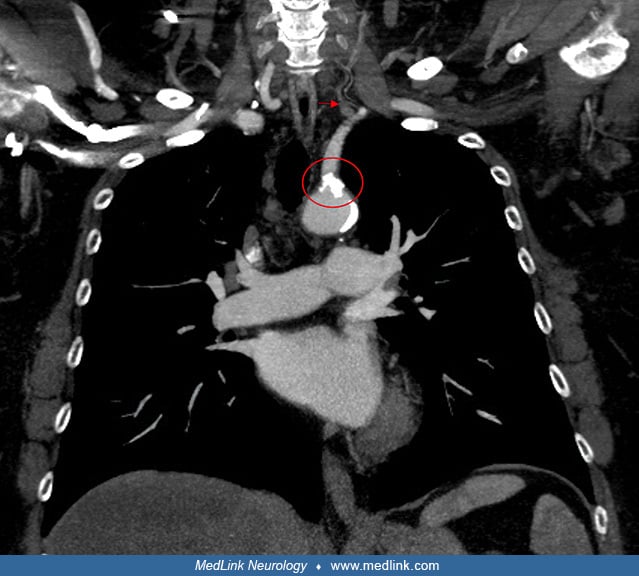
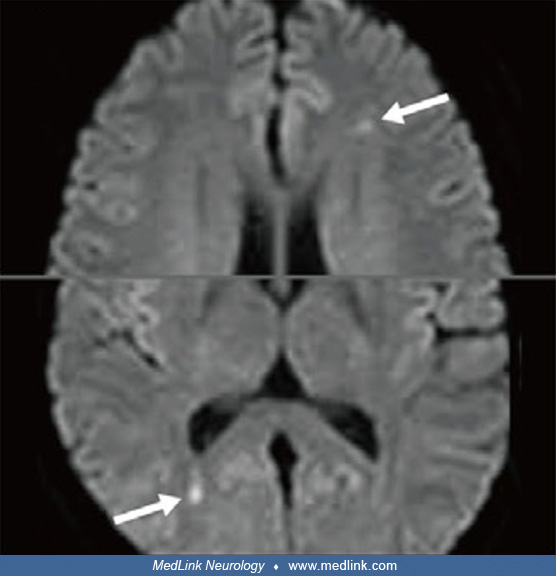
Enhancement in medial right temporal lobe due to varicella-zoster virus (CT)
Transverse CT image of the soft tissue head demonstrating faint enhancement along the medial right temporal lobe, measuring about 1.5 × 1.18 cm (arrow). The differential includes reactive or infectious processes, low-grade glioma, meningioma, and artifact. (Source: Gillette BT, Heilbronn CM. A rare case of vocal cord paralysis in the setting of Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Cureus 2023;15[3]:e36027. Creative Commons Attribution [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
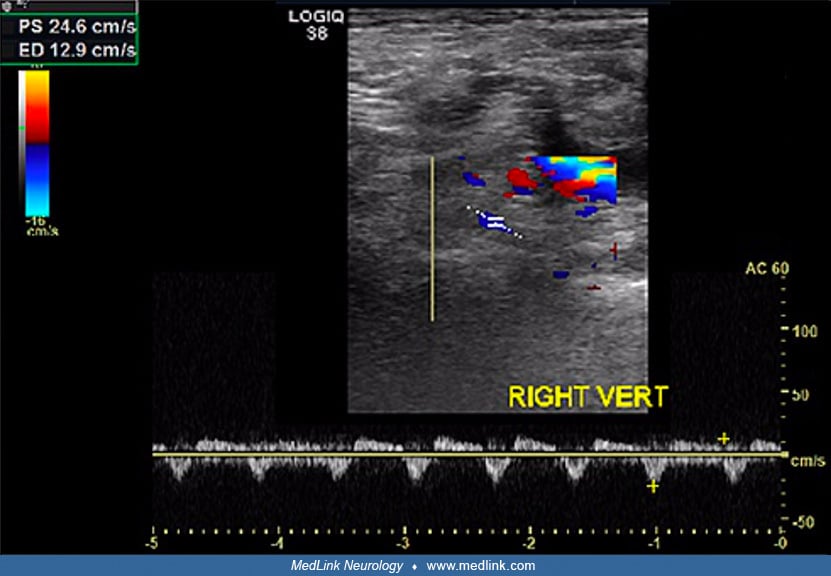
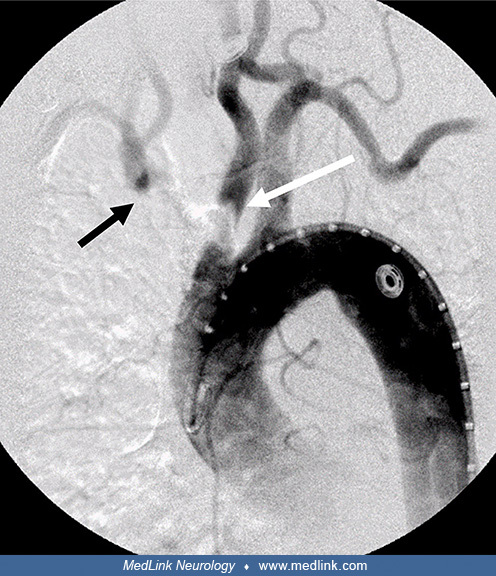
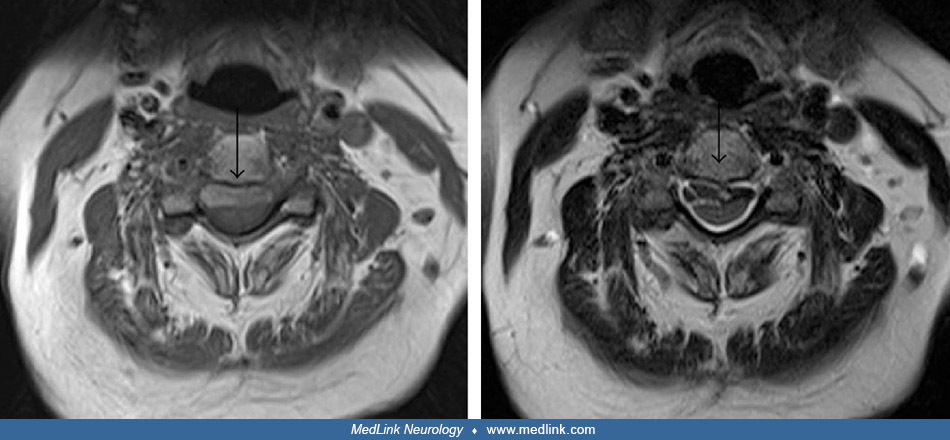
Enhancement of distal right internal auditory canal due to varicella-zoster virus (MRI)
Brain magnetic resonance image showing increased enhancement in the distal right internal auditory canal (arrow). (Source: Chou CC, Lo YT, Su HC, Chang CM. Fear of falling as a potential complication of Ramsay Hunt syndrome in older adults: a case report. BMC Geriatr 2022;22[1]:901. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.)
-

Media
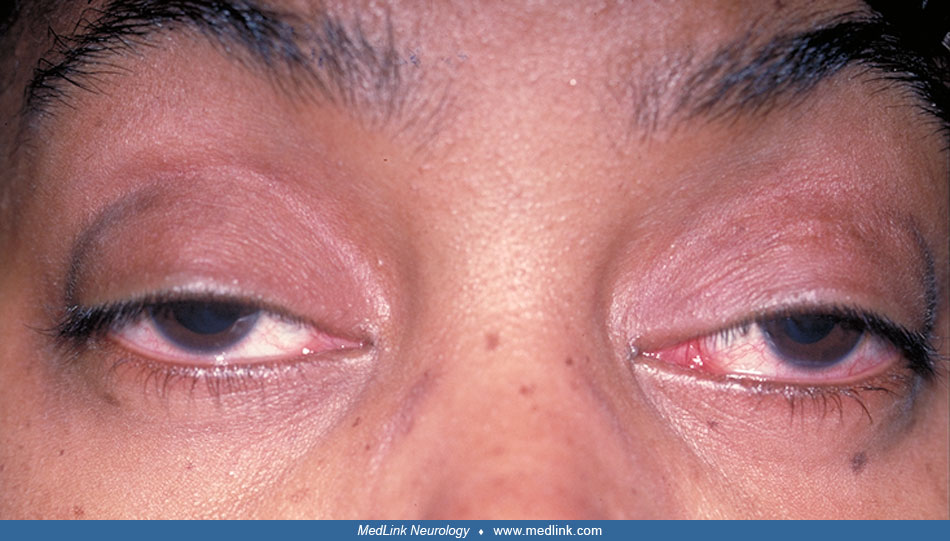
Ramsay Hunt syndrome (1-year follow-up)
One year after the patient’s Ramsay Hunt syndrome episode. Her facial palsy was considerably improved, and she received a Grade II score on the House-Brackmann Facial Paralysis Scale. (Source: Chou CC, Lo YT, Su HC, Chang CM. Fear of falling as a potential complication of Ramsay Hunt syndrome in older adults: a case report. BMC Geriatr 2022;22[1]:901. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International [CC-BY 4.0] license, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0. The image was cropped from the original.)
-

Media
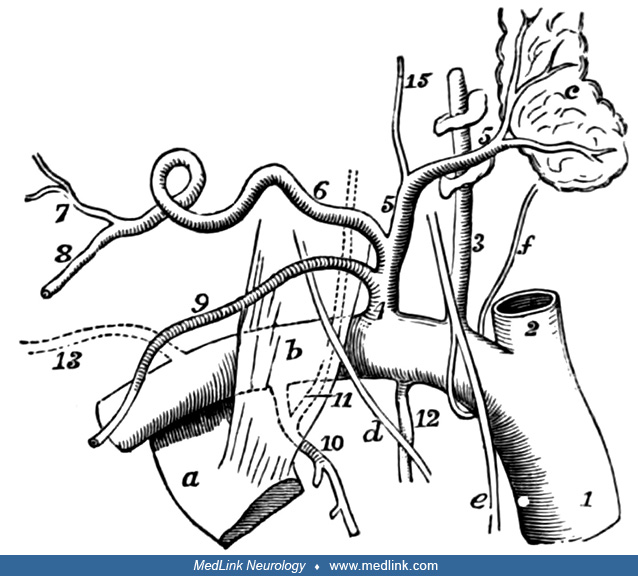
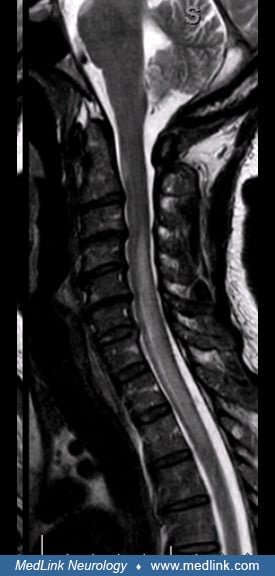
Anatomy of the oculosympathetic pathway
This is a 3-neuron chain. The first-order neuron originates in the hypothalamus and synapses in the intermediolateral cell column in the first thoracic segment. The second-order neuron originates in the spinal cord and synapses in the superior cervical ganglion. The third order neuron originates in the neck and terminates on the dilator muscle of the iris and in the Muller muscle in the upper lid. (Contributed by Dr. Jonathan Trobe from: Neuro-ophthalmology At Your Fingertips, https://fingertips.neuro-ophthalmology.med.umich.edu.)